Imaging technology
Micro CT
Nano CT
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
Immunoelectron Microscopy (IEM)
Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM)
Liquid-Phase Electron Microscopy (Liquid EM)
In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging
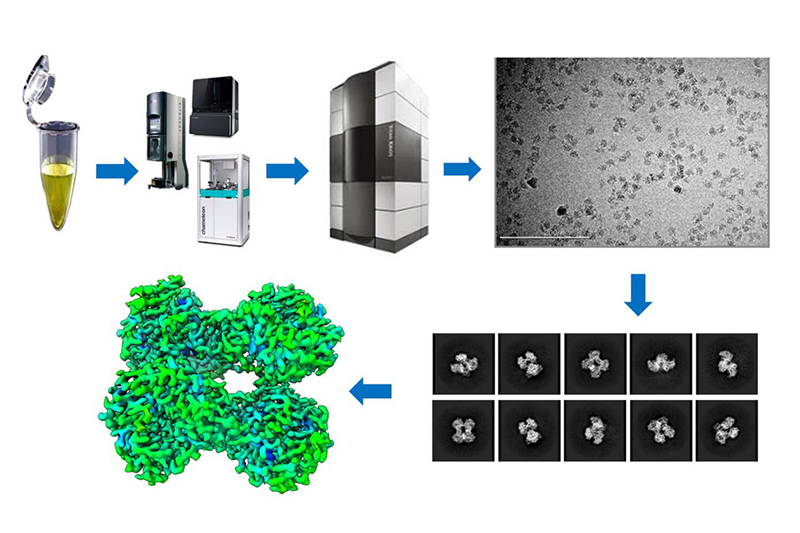
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a microscopic technique that involves observing samples using transmission electron microscopy at low temperatures. The samples are rapidly frozen and kept at low temperatures before being placed in the microscope. Highly coherent electrons are used as the light source, passing through the sample and the surrounding ice layers, and scattering in the process. The scattered signals are then captured by detectors and lens systems, processed to create an image, and analyzed to determine the structure of the sample.
Hong Kong Office:224 Waterloo Road, Kowloon Tong, Hong Kong (inside the Baptist University campus)
Shanghai Office:2F, 1788 Caoyang Road, Putuo District, Shanghai
Shanghai Office:2F, 1788 Caoyang Road, Putuo District, Shanghai
copyright © ROYAL BIOTECH All rights reserved.
